1. Free to leave the Cloud?
1.1. Dependence on suppliers
A common challenge for companies in the Cloud arena is to avoid dependency on their Cloud provider. This situation arises, however, when an organization becomes heavily dependent on a Cloud provider's specific tools and services, to the point where changing provider becomes both very difficult and expensive.
The underlying risks of cloud dependency :
- Dependence on proprietary tools and services that limit flexibility and innovation.
- High migration costs to transfer data and services to a new provider.
- Risk of data loss or operational disruption during the migration process.
1.2 Data sovereignty and compliance
Storing data in the Cloud implies that the data may be stored in a country with a different jurisdiction from the Data's country of origin, and therefore subject to different laws.
Underlying sovereignty risks :
- Legal and regulatory requirements: data stored in different countries must comply with varying legal and regulatory standards, which can be complex and difficult to manage.
- Risk of interrupted data access: geopolitical events or sanctions can potentially have an impact on data accessibility, leading to interruptions or loss of control of sensitive data stored abroad.
2. Pricing and cost management for Cloud services
2.1. Understanding hidden costs
Although Cloud services often emphasize scalability and pay-as-you-go pricing models, businesses need to be aware of potential hidden costs.
Acase study of 37signals' migration away from Cloud services reveals significant cost issues in Cloud storage. In 2022, the company spent $3.2 million on Cloud services, with almost $1 million allocated to storing eight petabytes of files on AWS S3. To reduce these expenses, 37signals plans to abandon cloud providers such as AWS and Google Cloud, hoping to save $7 million over five years. This approach, while entailing significant up-front expenditure on hardware and datacenter costs, is expected to deliver substantial savings over the initial recurring cost.
The company anticipates not only financial savings, but also benefits such asfaster hardware and cheaper storage expansion, as long as it can install the new servers in its existing datacenter.
Underlying cost risks :
- Budget overrun due to unforeseeable costs.
- Costs of data migration or API calls, which can add up.
2.2. Monitoring cost escalation
As a business grows, the costs of using Cloud services can escalate rapidly, especially if they are not managed effectively.
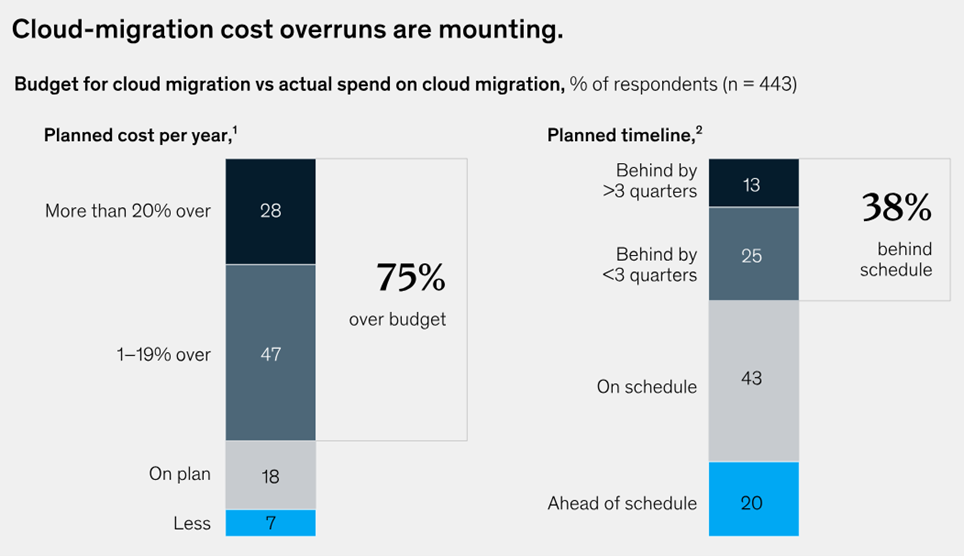
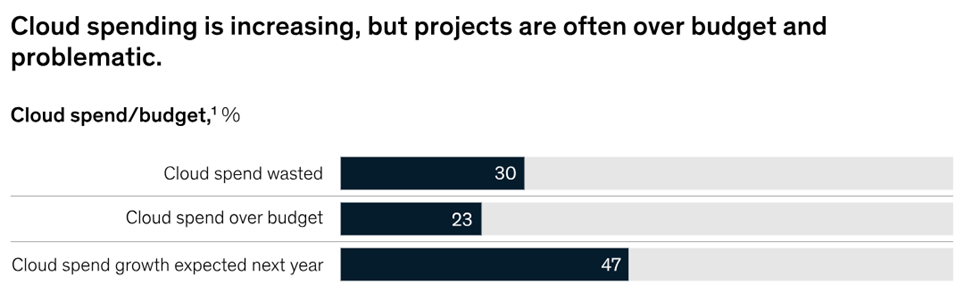
In McKinsey's report on cloud migration, we find that 75% of companies claim to have exceeded their budget, and 30% consider their cloud spending to have been unnecessary (see charts below).
The underlying risks of cost escalation :
- Budget allocations exceeded.
- Reduced profits due to higher operating costs.
3. Impact on human resources
A study by Les Echos on cloud migration highlights two main areas of concern:
- Human resources and skills management: the move to Cloud services is affecting the workforce, particularly those in traditional datacenter roles. These employees need new skills to manage the Cloud, requiring training in both technical skills and "soft skills" to adapt to project work and the Cloud environment. These functions can also be oriented towards cybersecurity and data protection.
- Governance and strategic planning: Effective migration to the Cloud requires strong governance and collaboration at all levels of the organization. Management must strategically guide this transition to align with the Cloud culture. Without this strategic planning and governance, the move to Cloud infrastructure could face major obstacles.
Underlying human resources risks :
- Skills shortages and labor migration.
- Operational disruption and resistance to change.
4. Choose the right technology: adopt Open Source solutions
Open Source technologies offer a viable alternative to Cloud services. These solutions enable organizations to exercise greater control over their IT infrastructure, offering flexibility and customization options to meet specific needs.
Advantages :
- Less dependence on suppliers.
- Better control of data and infrastructure.
- Potential long-term savings.
The underlying risks of Open Source solutions :
- Initial installation and migration costs.
- Potential compatibility problems with existing tools and services.
Conclusion
The Cloud offers many advantages, but companies need to remain vigilant against potential pitfalls. Dependence on Cloud providers, hidden and rising costs, and data sovereignty are just some of the challenges. Open Source solutions like Cloud Tiger can offer an alternative route to greater autonomy and control. By properly weighing up the pros and cons, it's imperative for companies to fully understand the risks involved and develop a strategy to mitigate them.
Ultimately, the choice to stay or leave the Cloud should be based on specific business needs, long-term strategies and a full understanding of the costs involved.
Additional resources : GitHub Cloud Tiger repository
powered by Advanced iFrame. Get the Pro version on CodeCanyon.
powered by Advanced iFrame. Get the Pro version on CodeCanyon.